جهت استعلام قیمت و مشاوره رایگان، تماس بگیرید
(09176050698 و 37742637-071)
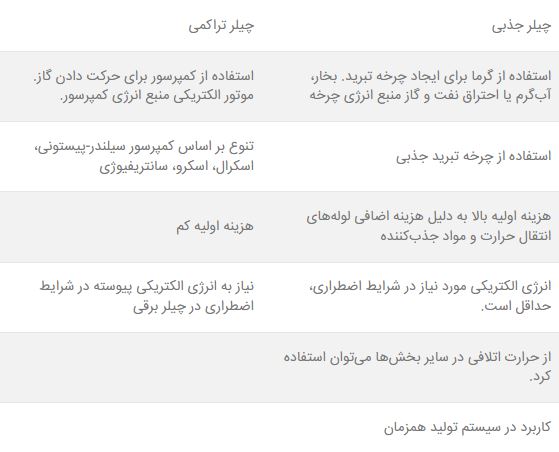
A chiller is a system that draws heat from a liquid using a compression refrigeration cycle or an absorption refrigeration cycle. This cooled liquid can be used in air conditioning equipment such as air conditioners and fan coils. Heat taken from water can be given to the environment or used to increase efficiency in heating applications.
The refrigerant gas of the chillers in the condenser is cooled by three methods of cold water, air cooling and evaporation.
Chiller is used in both air conditioning and industrial fields.
In the application of air conditioning, chilled water in the chiller is used to cool and reduce air humidity in medium to large office, industrial and commercial units.

In industrial applications, chilled water is used for controlled cooling of factory products, mechanisms and machinery. For example, industrial chillers are used in the plastics, molding, casting, chemical, food, pharmaceutical and other industries.


Some of the applications of industrial chillers are as follows:
1. Plastics industry: Cooling of hot plastics during molding processes such as injection, extrusion and blowing
2. Printing industry: Cooling rollers that are heated due to friction and ink baking oven.
3. Medical industry (MRI machine): The MRI machine needs cooling to function properly.
4- Laser cutting industry: Due to the function of laser in cutting metals, a lot of heat is generated and cooling is required.
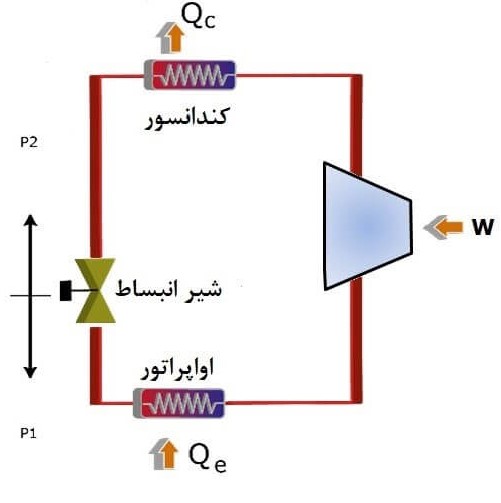
Compression chiller performs cooling operation based on refrigerant gas density. First, the gas pressure is increased by the compressor and then enters the condenser and turns into liquid by losing heat, and then enters the evaporator through the expansion valve and decreases the temperature and pressure, and receives the heat of the water adjacent to the evaporator. As a result, cooled water is produced in the chiller.
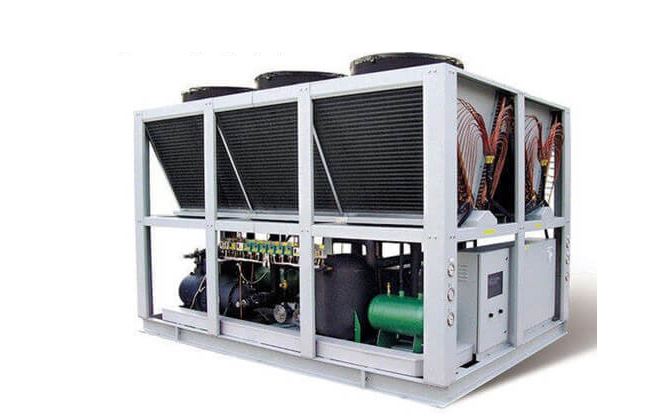
Compression chiller components
Compression chiller has different parts, the most important of which are: compressor, condenser, evaporator, expansion valve, shock absorber, electrical panel.
The following figure summarizes the compression refrigeration cycle.
The compression chiller structure consists of four main parts of the compression refrigeration cycle. These four parts are the compressor, the evaporator, the condenser and the expansion valve. In the compression refrigeration cycle, HFC and HCFC gases are commonly used for refrigeration. The compressor acts as the driving force of this cycle and the compression chiller generates cooled water with mechanical energy. The water cools in the chiller evaporator. The evaporator used is shell and tube heat exchanger (shell and tube) or plate type.
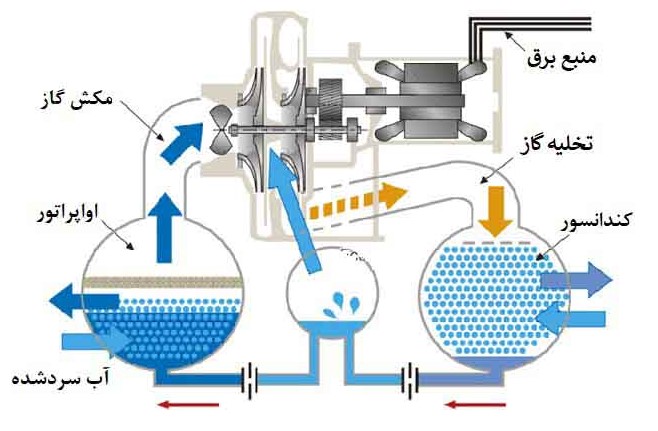
The principle of operation of the absorption and compression chiller is the same, with the difference that another method is used to increase the pressure of the exhaust gas from the evaporator with the aim of transferring it to the condenser. Water vapor after the evaporator is absorbed by a liquid such as lithium bromide. The adsorbent solution and water are transferred to the heat generator by a pump. The solution is then heated, and as a result, the solution water evaporates and enters the condenser. The rest of the cycle is the same as the compression cycle.
Waste heat in other sources can be used as a heat generator, which increases efficiency.
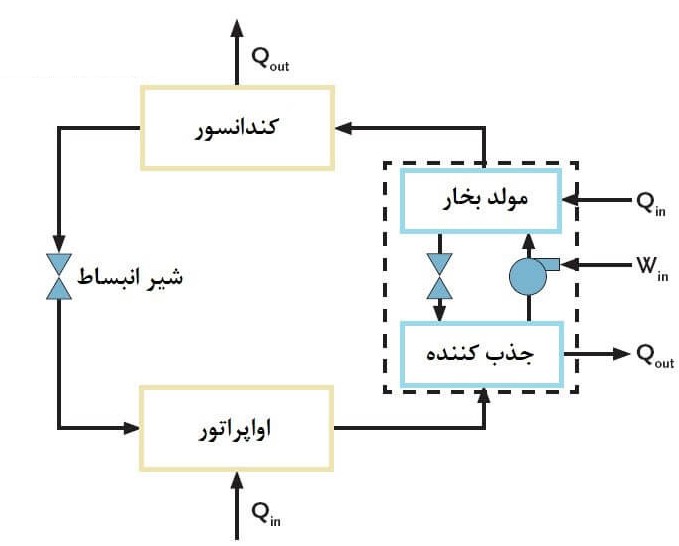
Absorption chiller has different parts, the most important of which are: absorber, steam generator, condenser, evaporator, expansion valve, shock absorber, electrical panel.
The following figure illustrates the adsorption refrigeration cycle.
دیدگاهها
هیچ دیدگاهی برای این محصول نوشته نشده است.